METHODS
Course Patterns
Students can complete a major or a minor. The units are sequential.
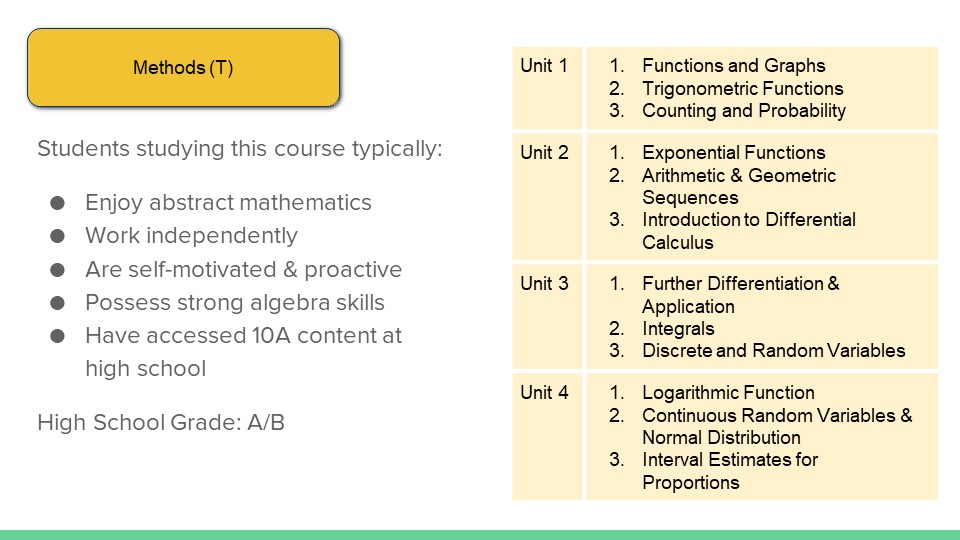
Unit 1
Topic 1: Functions and Graphs
Topic 2: Trigonometric Functions
Topic 3: Counting and Probability
Reviews the basic algebra required for successful study of functions and calculus. Simple relationships between variable quantities used to introduce the concepts of a function and its graph. The study of probability and statistics reviews the fundamentals of probability, and introduces the concepts of conditional probability and independence. The study of the trigonometric functions begins with the unit circle using degrees and the trigonometry of triangles. Radian measure is introduced, and the graphs and applications of the trigonometric functions are explored.
Unit 2
Topic 1: Exponential Functions
Topic 2: Arithmetic & Geometric Sequences
Topic 3: Introduction to Differential Calculus
Introduces exponential functions, their properties and graphs. Arithmetic and geometric sequences and their applications are introduced. Rates of change are introduced, and the concept of the derivative as an ‘instantaneous rate of change’. Concepts are reinforced numerically, geometrically, and algebraically. This first calculus topic concludes with derivatives of polynomial functions, using simple applications of the derivative to sketch curves, calculate slopes and equations of tangents, determine instantaneous velocities, and solve optimisation problems.
Unit 3
Topic 1: Further Differentiation & Application
Topic 2: Integrals
Topic 3: Discrete and Random Variables
Continues the study of calculus, introducing the derivatives of exponential and trigonometric functions and their applications, some basic differentiation techniques and the concept of a second derivative and applications. The unit includes integration as a way of calculating areas. The fundamental theorem of calculus is emphasised. Discrete random variables are introduced in modelling processes involving chance and variation.
Unit 4
Topic 1: Logarithmic Function
Topic 2: Continuous Random Variables & Normal Distribution
Topic 3: Interval Estimates for Proportions
introduces the logarithmic function and its derivative. Continuous random variables and their applications are introduced. In this unit students are introduced to one of the most important parts of statistics, statistical inference, where the goal is to estimate an un-known parameter associated with a population using a sample of that population. In this unit, inference is restricted to estimating proportions in two-outcome populations.
